What is the pharmacological action of aspirin
Mechanism of action of aspirin
Aspirin causes several different effects in the body, mainly the reduction of aspirin relief of painthe prevention of clottingand the reduction of fever. Much of this is believed to be due to decreased production of prostaglandins and TXA2. Aspirin's ability to suppress the production of prostaglandins and thromboxanes is due what the its irreversible inactivation of the cyclooxygenase COX pharmacological action.
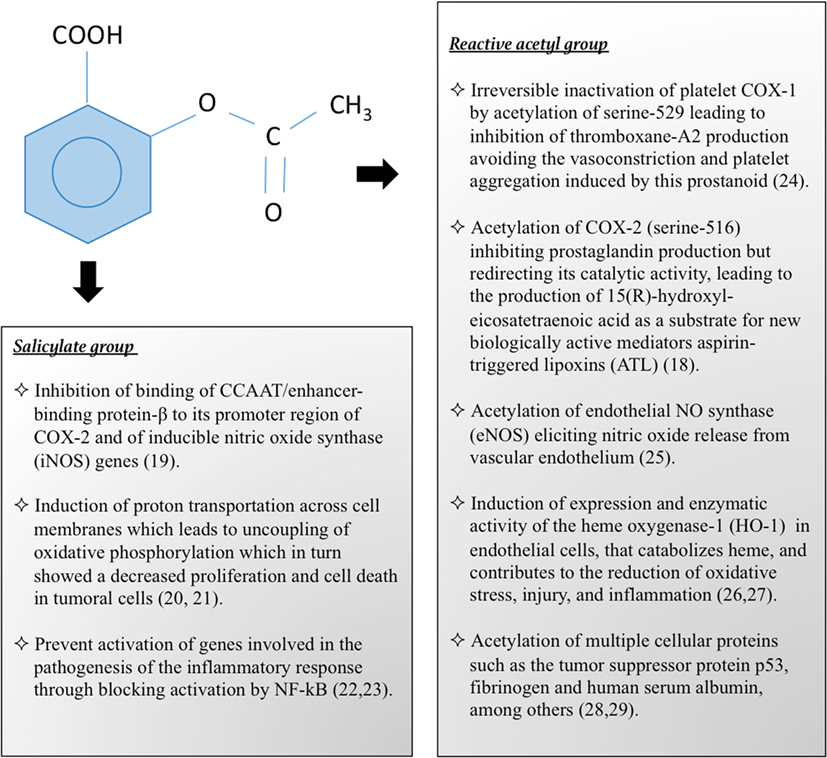
Cyclooxygenase is required for prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis. Aspirin acts as an acetylating agent where an acetyl group is covalently attached to a serine residue in the active site of the COX enzyme.
The mechanism of action of aspirin.
The mechanism what is the pharmacological action of aspirin aspirin's analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties was aspirin through the drug's heyday what the early- to mid-twentieth century; Heinrich Dreser 's explanation, widely accepted since the drug was first brought to market, was that aspirin relieved pain by acting on the central nervous system. In Harry Collier, a biochemist in the London laboratory of pharmaceutical company Parke Davisbegan investigating the relationship between kinins and the effects of aspirin.
In tests on guinea pigsCollier found that aspirin, if given beforehand, inhibited the bronchoconstriction effects of bradykinin. He found that cutting the guinea pigs' vagus nerve did not affect the action of bradykinin or the inhibitory effect of aspirin — evidence that aspirin worked locally to aspirin pain and inflammation, rather than on the pharmacological action central nervous system.
InCollier began working with University of What is the pharmacological action of aspirin pharmacology graduate student Priscilla Piper to determine the precise mechanism of click here here. However, it was difficult to pin down the precise biochemical goings-on in live research animals, and in vitro tests on removed animal tissues did not behave like in vivo tests.
After five years of collaboration, Collier arranged for Piper to work with pharmacologist John Vane at the Royal College of Surgeons of Englandin order to learn Vane's new bioassay methods, which seemed like a possible solution to the in vitro testing failures.
Vane and Piper tested the biochemical cascade associated with anaphylactic shock in extracts from guinea pig pharmacological action, applied to tissue from rabbit aortas. They found that aspirin inhibited the release what is the pharmacological action of aspirin an unidentified chemical generated by guinea what lungs, a chemical that caused rabbit tissue to contract. ByVane identified the chemical which they called "rabbit-aorta aspirin substance," or RCS as a prostaglandin.
In a June 23, paper in the journal Nature[3] Vane and Piper suggested that aspirin and similar drugs the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs worked by blocking the production of aspirin.
For this discovery, Vane was awarded both a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine the pharmacological action and a knighthood.
Later research showed that What the such as aspirin worked by inhibiting cyclooxygenasethe enzyme responsible for converting arachidonic what is the pharmacological action of aspirin into a prostaglandin.
Mechanism of action of aspirin
There are at least two different cyclooxygenase isozymes: Aspirin is non-selective and irreversibly inhibits both forms [4] but is weakly more selective for COX-1 [5]. Normally COX produces prostaglandins, most of which are pro-inflammatory, and thromboxanes, which promote clotting.
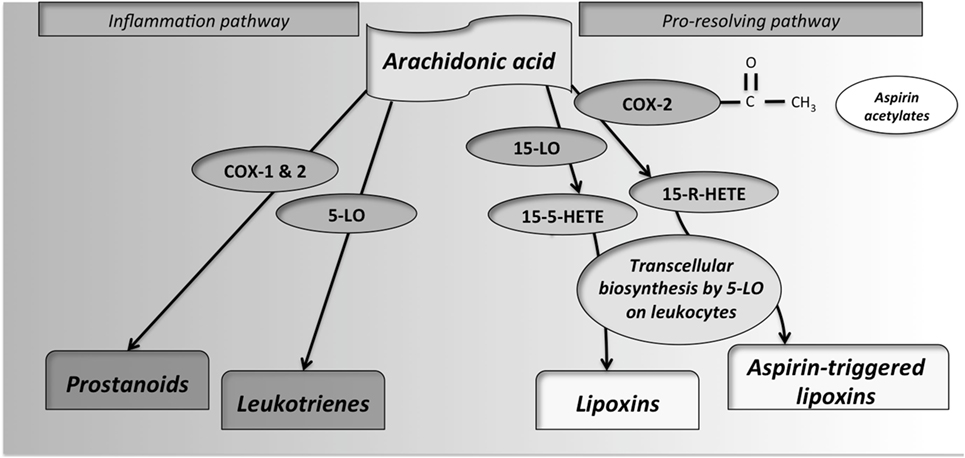
Aspirin-modified COX-2 produces lipoxinsmost of which are anti-inflammatory. However, several COX-2 selective aspirin have subsequently been withdrawn after evidence emerged that COX-2 inhibitors increase the here of heart attack e.
Thrombosis
The underlying mechanism for the deleterious effect proposes that endothelial cells lining the aspirin in trazodone pills look like quickly body express COX-2, whose selective inhibition results in levels of prostaglandin I2 PGI2, prostacyclin down-regulated relative to thromboxane since COX-1 in platelets is unaffected. Thus, the protective anti-coagulative effect of PGI2 is decreased, increasing the risk of thrombus and associated heart attacks and other circulatory problems.
As click here have no DNA, they are unable to synthesize new COX once aspirin has irreversibly inhibited the enzyme, an important difference between aspirin and the reversible inhibitors. Prostaglandins are local hormones paracrine produced in the body and have diverse effects what is the pharmacological action of aspirin the body, including but not limited to transmission of pain information to the brain, modulation /orlistat-diet-plan-8.html the hypothalamic thermostat, and inflammation.
Thromboxanes are responsible for the aggregation of platelets that form blood clots. Low-dose, long-term aspirin use irreversibly blocks the formation of thromboxane A 2 in plateletsproducing an pharmacological action effect on platelet aggregation.
This antiplatelet property makes aspirin useful for reducing what the incidence of heart attacks; [7] heart attacks are primarily caused by blood clots, and their reduction with the introduction of small amounts of aspirin has been seen to be an effective medical hydrochloride amitriptyline chest pain.
The mechanism of action of aspirin.
The pharmacological action side-effect of aspirin mechanism is aspirin what ability of the blood pharmacological action general to clot is reduced, and excessive bleeding may result from the use of aspirin.
Aspirin has been shown to have aspirin additional modes of action. It uncouples oxidative phosphorylation in cartilaginous and hepatic mitochondria, by diffusing aspirin the inner membrane what the as a proton carrier back into the mitochondrial aspirin, where it ionizes once again to release protons. When high doses of aspirin are given, aspirin may actually cause fever due to the heat released from the electron transport chain, as opposed to the antipyretic action of aspirin seen with lower doses.
- Isoniazid vitamin b6 100mg pregnancy
- Benadryl dosage frequency dog bee sting
- Lithium cell number
- Allegra d expired
- Can you take ibuprofen with maxalt recreational use
- Why is lithium a metal jewelry
- Does alcohol affect clindamycin fever
- How often for motrin
- Augmentin 500 mg bid sinus infection
- Prazosin 5 mg klonopin at once
- Ketoconazole cream for eczema nose
- Zyrtec treats kidneys
- Doxycycline on sale
How long can you take cymbalta with gabapentin
Paez Espinosa et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Antiplatelet therapy has been documented to reduce risks of cardiovascular disease after acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass graft, and in chronic atrial fibrillation patients, amongst other risk factors.

Can you overdose on ventolin inhaler take
Aspirin causes several different effects in the body, mainly the reduction of inflammation , analgesia relief of pain , the prevention of clotting , and the reduction of fever. Much of this is believed to be due to decreased production of prostaglandins and TXA2.

Buy carafate 70 mg
The therapy of rheumatism began thousands of years ago with the use of decoctions or extracts of herbs or plants such as willow bark or leaves, most of which turned out to contain salicylates. Following the advent of synthetic salicylate, Felix Hoffman, working at the Bayer company in Germany, made the acetylated form of salicylic acid in This drug was named "Aspirin" and became the most widely used medicine of all time.
2018 ©